Fitness for Service assessment of riser unit of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)
Fitness for Service assessment of riser unit of Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC)
Fitness for service assessment of critical systems of refineries is an important activity during maintenance regimes. After the manual inspections and NDE evaluations, any potential defects such as corrosion, creep or fatigue damage, dents etc., are detected and sized. Here we present a case of fitness for service evaluation of a riser in the reactor section of a fluid catalytic cracking unit of a refinery. FFS evaluation, work done at ProSIM included creep life assessment towards remaining life assessment and extension.
ProSIM is a company providing engineering outsourcing services /engineering design services including structural integrity assessment services. Range of services include CAE services (Computer aided engineering services), FEA services (Finite element analysis services), fitness for service evaluation including FFS level-3 evaluation, remaining life assessment service and remaining life extension service (RLA/RLE services).
In the riser section of FCC unit of the refinery studied in this case study, hot spots were observed by thermal imaging, due to cracks in the refractory lining. Temperatures were in the range of 360°C to 380°C due to refractory damage. Quite a large area of the refinery was affected by the damage. Mandate to ProSIM was to analyse the causes of damage, carryout FFS asper API 579, estimate the remaining life of riser including the creep damage, and provide guidelines for repair and reuse of the riser in the FCC for remaining life extension. Towards this, ProSIM conducted detailed finite element analysis for design and operating conditions of the FCC unit and used the MPC Omega method as detailed in API-579-1/ASME FFS-1.
Key Findings
Our study, using coupled thermo-mechanical finite element analysis, identified significant stress concentrations at two hotspot locations in the riserreactor section. One of the hotspots was at 350°C and other at 380°C. Stress levels at the hotspot operating at 350°C remained well within permissible limits with a remaining lifespan exceeding 25 years under operating conditions.
In the hotspot operating at 380°C, the stress levels were found to be critical, indicating a functional lifespan of less than 3 years. As part of the solution, we studied providing effective cooling solutions. Introducing efficient cooling methods significantly reduced the stress levels, thereby extending the projected operational life beyond 25 years.
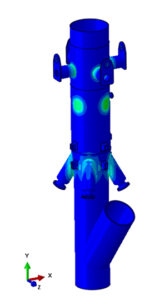
Figure showing the stress hotspots in FCC predicted using finite element analysis.